Short marketing description (for website / catalog headline)
High-purity Sodium Nitrate — a versatile, cost-effective nitrogen source and industrial salt with wide applications across fertilizers, glass & ceramic manufacture, heat-treatment baths, and specialty chemical processes. Engineered for consistent quality, excellent solubility, and reliable performance — with options for bulk, bagged, and custom packaging.
2) Key product features (quick bullets)
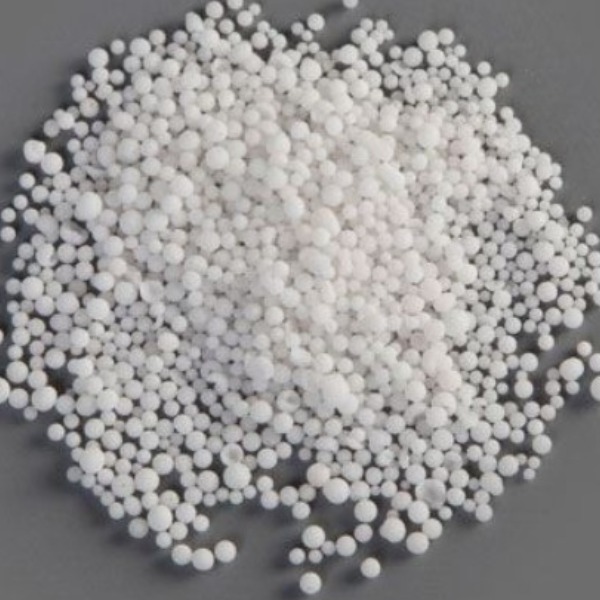
Chemical name: Sodium Nitrate (NaNO₃)
Purity: Industrial / technical grades (specify e.g., 98%+ available; customize per customer)
Appearance: White crystalline powder or granular salt
Solubility: Highly soluble in water — easy to dissolve and dose
Packaging: 25 kg bags, 50 kg bags, jumbo bags (FIBC), bulk tanker/containers (as per logistics)
Shelf life: Stable if stored dry and protected from humidity
Custom services: COA, SDS, sample batches, technical support for blending & application
3) Main applications (concise)
Fertilizer & soil amendment: Nitrogen source (used alone or blended with other fertilizers).
Glass & ceramics: Fluxing agent, helps control melt characteristics and clarity.
Heat treatment & metal processing: As a component in salt baths for annealing and quenching operations.
Chemical industry & lab reagents: Feedstock for certain nitrate-based syntheses and catalysts.
Other industrial uses: Select oxidizing agent applications (note: regulated uses require controls).
4) Environmental benefits — how sodium nitrate can be used more sustainably
(Important: nitrates themselves can cause environmental harm if misused; below lists benefits when used responsibly.)
Efficient nitrogen delivery: When applied at the right rate and timing, sodium nitrate supplies plant-available nitrogen with predictable release, supporting crop yields and efficient fertilizer use.
Reduced ammonia volatilization: Compared with some ammoniacal fertilizers, nitrate-based nitrogen avoids volatilization losses as ammonia, improving nitrogen-use efficiency in many conditions.
Compatibility with fertigation: Easy solubility makes it suitable for drip/fertigation systems — enabling precise dosing and reducing over-application. Precise application reduces runoff risk when best practices are followed.
Enables localized dosing & precision agriculture: Works well with sensor-based/precision systems to match crop demand, lowering overall N inputs.
Lower transport weight for equivalent nutrient delivery (in specific supply chains): In regions where logistics and local blending optimize transport, overall supply-chain emissions can be reduced.
Environmental caution: nitrates are mobile in soil and can contaminate groundwater or cause eutrophication if over-applied or mismanaged. Responsible recommendations and farmer training are essential.
5) Economic benefits — why buyers choose sodium nitrate
High nutrient efficiency: Predictable nitrate form reduces losses; growers may see better return-per-kg N.
Flexibility in blending: Can be blended with other salts or micro-nutrients to produce tailored fertilizers, increasing product value.
Stable storage & handling: Long shelf life reduces product waste and inventory losses.
Multiple industrial markets: Demand across agriculture, glass, metal treatment, and chemical sectors reduces market risk for suppliers.
Competitive supply options: Bulk distribution and local warehousing (e.g., Gujarat/West India) can lower landed cost for industrial buyers.
Value-added services: Offering COA, SDS, sampling, and technical support increases conversion and customer retention.
6) Environmental risk management & best-practice recommendations (what to communicate to customers)
Use soil tests & agronomic recommendations — always match application to crop need.
Encourage split applications or fertigation rather than one large dose.
Promote buffer zones and runoff controls near water bodies.
Provide product SDS and safe handling training to customers and transporters.
Offer controlled-release blends or mixed formulations to reduce leaching (if available).
End-of-life & spills: Clear instructions for containment and neutralization; keep dry and avoid release to waterways.
Fertilizers / Agriculture
Source of nitrate-nitrogen for high-value crops (horticulture, vegetables, fruit). Fast-release nitrate source; commonly used in fertigation and foliar feeds.
Pyrotechnics & Explosives (oxidizer)
Used as an oxidizer in fireworks, pyrotechnic compositions and some explosives formulations (handled under strict regulation).
Metal heat treatment & metallurgy
Used in salt baths for heat treatment (nitriding/annealing/quenching salts) and as a component in certain metal finishing processes.
Glass & ceramics
Fluxing agent and for specialty glass formulations.
Food curing / preservation (food grade)
Historically used in meat curing to develop color and inhibit bacterial growth (use is regulated — follow local food safety rules).
Chemical manufacturing / reagent
Raw material for nitric acid production (in some routes), nitration reactions, dyes, and specialty chemicals.
Laboratory reagent
Analytical and synthetic chemistry use where nitrate anion is required.
Corrosion inhibition & concrete additives (specialty uses)
In some concrete admixtures and corrosion-control formulations (application-specific).
Wastewater / industrial process uses
Employed in some processes for nitrate dosing or where controlled oxidation is needed.
Typical specifications (example — adjust per your supplier)
Assay (NaNO₃): 99% min (for technical grade)
Moisture: ≤0.5–1.0%
NaCl, Na₂SO₄ and insolubles: specified limits depending on grade
Particle size: granular or powdered options available
(If you want, I can format a full spec table for your exact grade — tell me the purity and target market and I’ll produce it now.)
Safety, storage & handling (important)
Oxidizer: Keep away from combustible and organic materials — contact can increase fire risk.
Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area in tightly closed containers. Avoid moisture and contamination.
Handling: Use non-sparking tools; grounding and bonding recommended for powder handling.
PPE: Gloves, eye protection, dust mask/respirator when dusty.
First aid: If inhaled — move to fresh air. In case of eye contact — rinse with water and seek medical attention. For ingestion — seek medical advice.
Disposal: Dispose according to local regulations; do not release large quantities to environment.
Documents to provide to customers: SDS (Safety Data Sheet), COA (Certificate of Analysis), and where food grade is claimed — relevant food-safety certificates.Fertilizers / Agriculture
Source of nitrate-nitrogen for high-value crops (horticulture, vegetables, fruit). Fast-release nitrate source; commonly used in fertigation and foliar feeds.
Pyrotechnics & Explosives (oxidizer)
Used as an oxidizer in fireworks, pyrotechnic compositions and some explosives formulations (handled under strict regulation).
Metal heat treatment & metallurgy
Used in salt baths for heat treatment (nitriding/annealing/quenching salts) and as a component in certain metal finishing processes.
Glass & ceramics
Fluxing agent and for specialty glass formulations.
Food curing / preservation (food grade)
Historically used in meat curing to develop color and inhibit bacterial growth (use is regulated — follow local food safety rules).
Chemical manufacturing / reagent
Raw material for nitric acid production (in some routes), nitration reactions, dyes, and specialty chemicals.
Laboratory reagent
Analytical and synthetic chemistry use where nitrate anion is required.
Corrosion inhibition & concrete additives (specialty uses)
In some concrete admixtures and corrosion-control formulations (application-specific).
Wastewater / industrial process uses
Employed in some processes for nitrate dosing or where controlled oxidation is needed.
Typical specifications (example — adjust per your supplier)
Assay (NaNO₃): 99% min (for technical grade)
Moisture: ≤0.5–1.0%
NaCl, Na₂SO₄ and insolubles: specified limits depending on grade
Particle size: granular or powdered options available
(If you want, I can format a full spec table for your exact grade — tell me the purity and target market and I’ll produce it now.)
Safety, storage & handling (important)
Oxidizer: Keep away from combustible and organic materials — contact can increase fire risk.
Storage: Store in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area in tightly closed containers. Avoid moisture and contamination.
Handling: Use non-sparking tools; grounding and bonding recommended for powder handling.
PPE: Gloves, eye protection, dust mask/respirator when dusty.
First aid: If inhaled — move to fresh air. In case of eye contact — rinse with water and seek medical attention. For ingestion — seek medical advice.
Disposal: Dispose according to local regulations; do not release large quantities to environment.
Documents to provide to customers: SDS (Safety Data Sheet), COA (Certificate of Analysis), and where food grade is claimed — relevant food-safety certificates.
Keywords
Safe handling and storage of sodium nitrate
Use of Sodium Nitrate in pyrotechnics and explosives
Sodium Nitrate in chemical manufacturing processes
Sodium Nitrate food grade preservation applications
Environmental benefits of nitrate-based fertilizers
Sodium Nitrate for heat treatment baths
Bulk Sodium Nitrate packaging Gujarat India
Sodium Nitrate for glass and ceramic manufacturing
Sodium Nitrate fertilizers and soil amendments
High-purity Sodium Nitrate for industrial use